Structural analysis of clastic dikes using Structure from Motion - Multi-View Stereo: a case-study in the Paraná Basin, southeastern Brazil
Full paper published at Brazilian Journal of Geology. I supervised Mariana Busarello during her undergraduate degree monograph on the 3D model generation and analysis.
Abstract
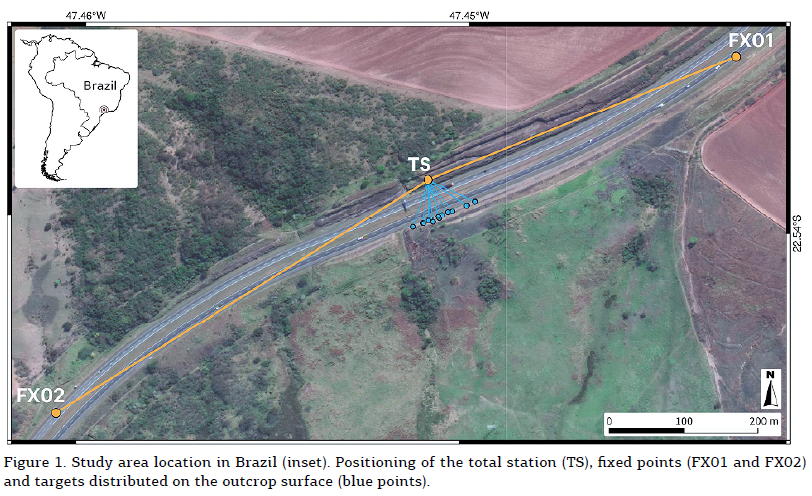
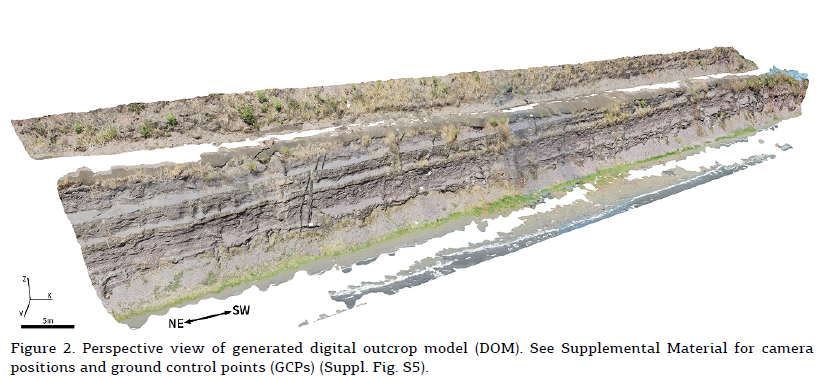
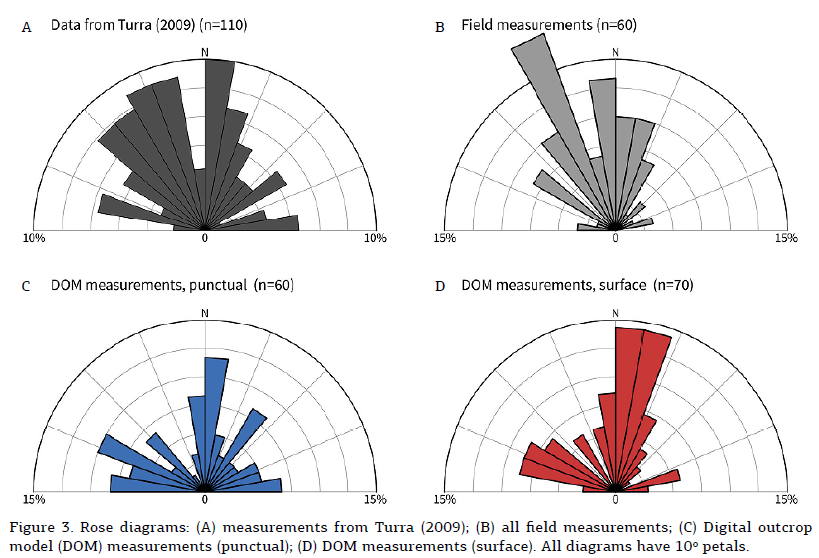
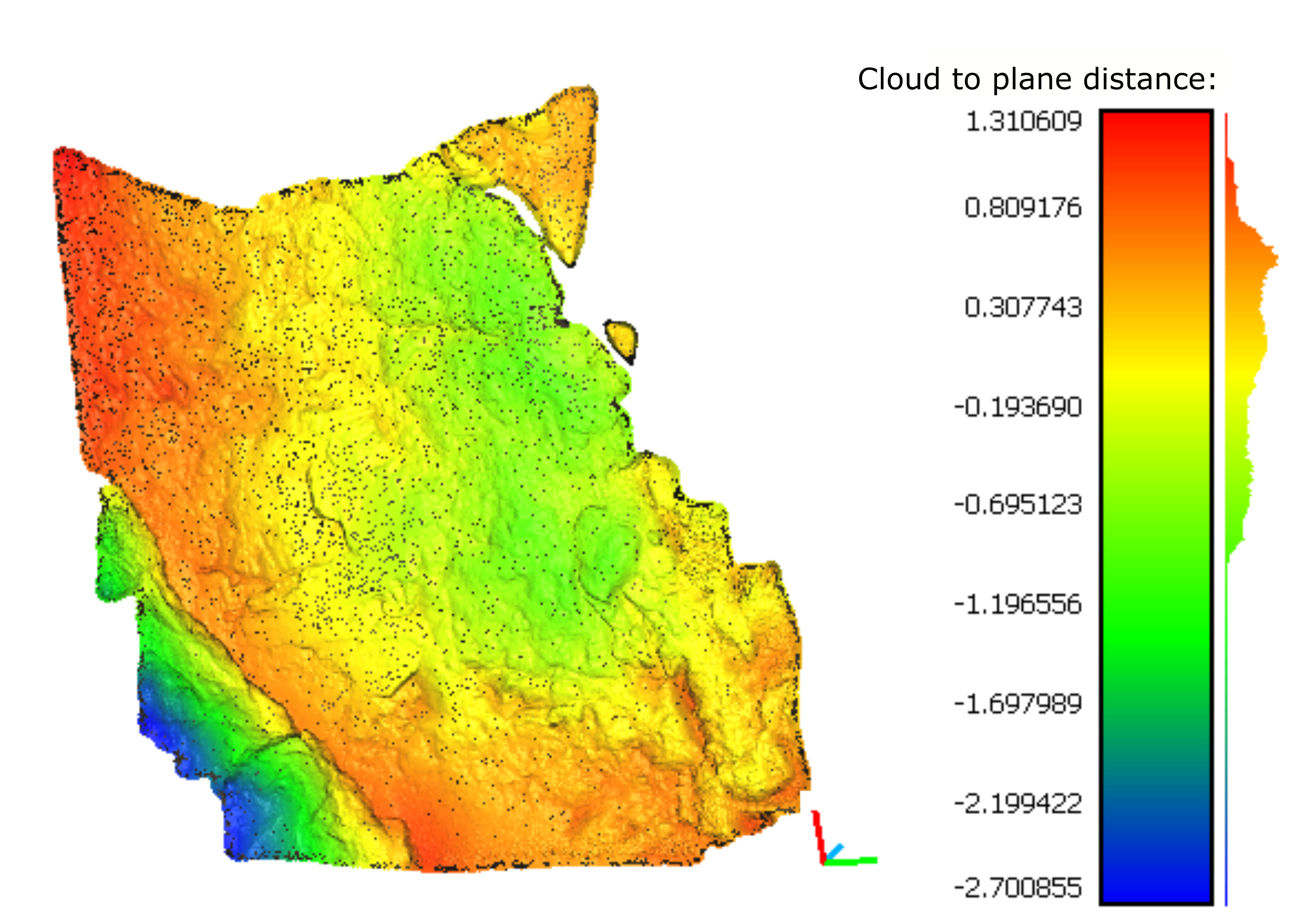
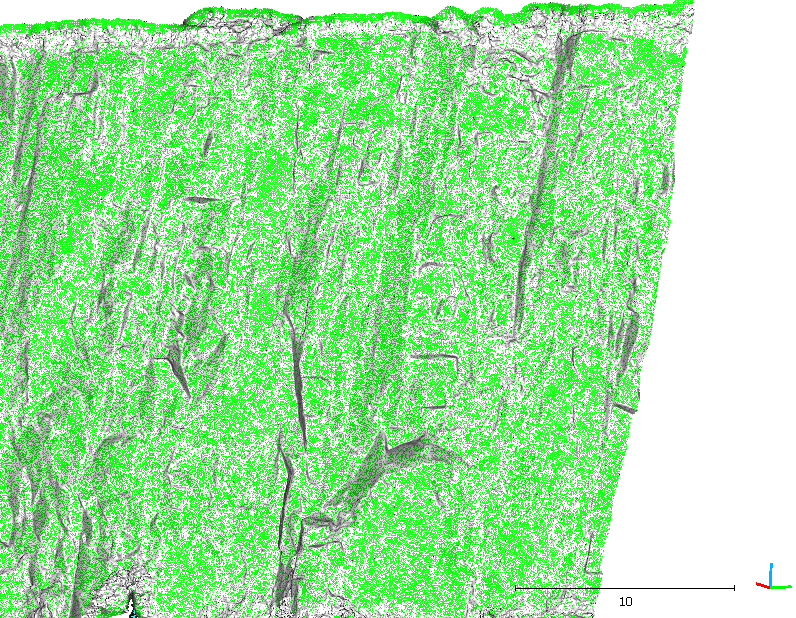
This work presents the development of a three-dimensional (3D) model of an outcrop of the Corumbataí Formation (Permian, Paraná Basin, Brazil) using Structure from Motion - Multi-View Stereo (SfM-MVS) technique in order to provide a structural analysis of clastic dikes cutting through siltstone layers. While traditional photogrammetry requires the user to input a series of parameters related to the camera orientation and its characteristics (such as focal distance), in SfM-MVS the scene geometry, camera position and orientations are automatically determined by a bundle adjustment, an iterative procedure based on a set of overlapping images. It is considered a low-cost technique in terms of hardware and software, also being able to provide point density and accuracy on par to the ones obtained withTerrestrial Laser Scanning. The results acquired on this research have good agreement with previous works, yielding a NNW main orientation for the dikes measured in the field and on the 3D model. The development of this work showed that SfM-MVS use and practice on geosciences still needs more studies on the optimization of the involved parameters (such as camera orientation, image overlap and angle of illumination), which, when accomplished, will result in less processing time and more accurate models.
Project Details
Date: Dec 1, 2018
Author: Viana, CD; Grohmann, CH; Busarello, MST & Garcia, GPP
Categories: PhD
Tagged: Clastic dikes, SfM, Digital Outcrop Model, Photogrammetry, Structural Geology
Journal/Event: Brazilian Journal of Geology, vol.48, n.4, pp.839-852
Website: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S2317-48892018000400839&lng=en&nrm=iso