Algorithms for extraction of structural attitudes from 3D outcrop models
Full paper published at Computers & Geosciences as part of MSc in Geotectonics at IGc-USP.
Abstract
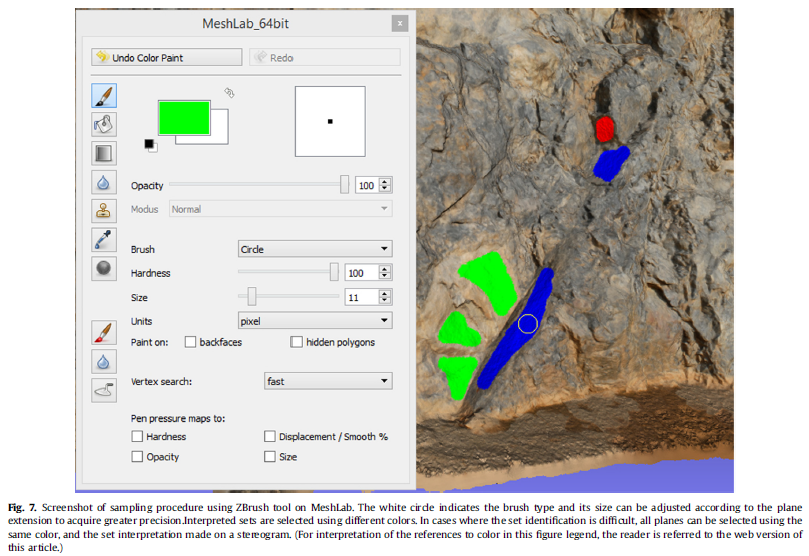
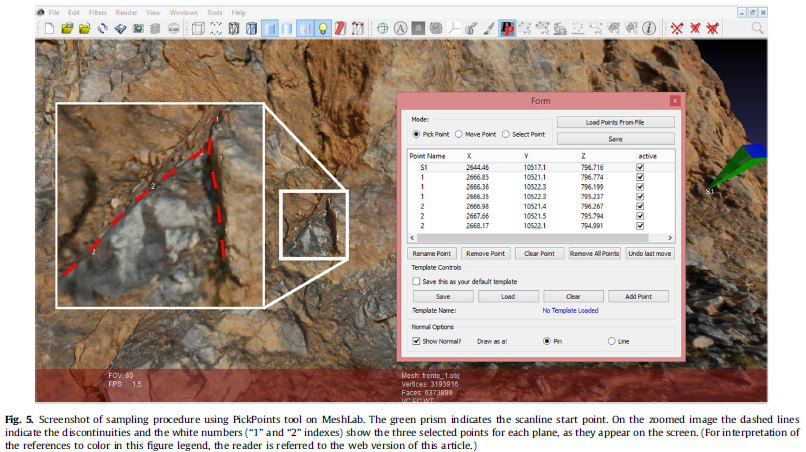
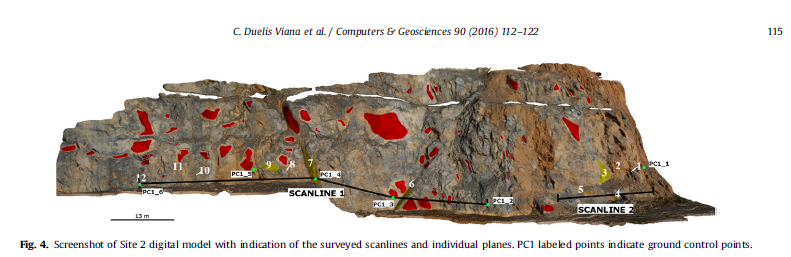
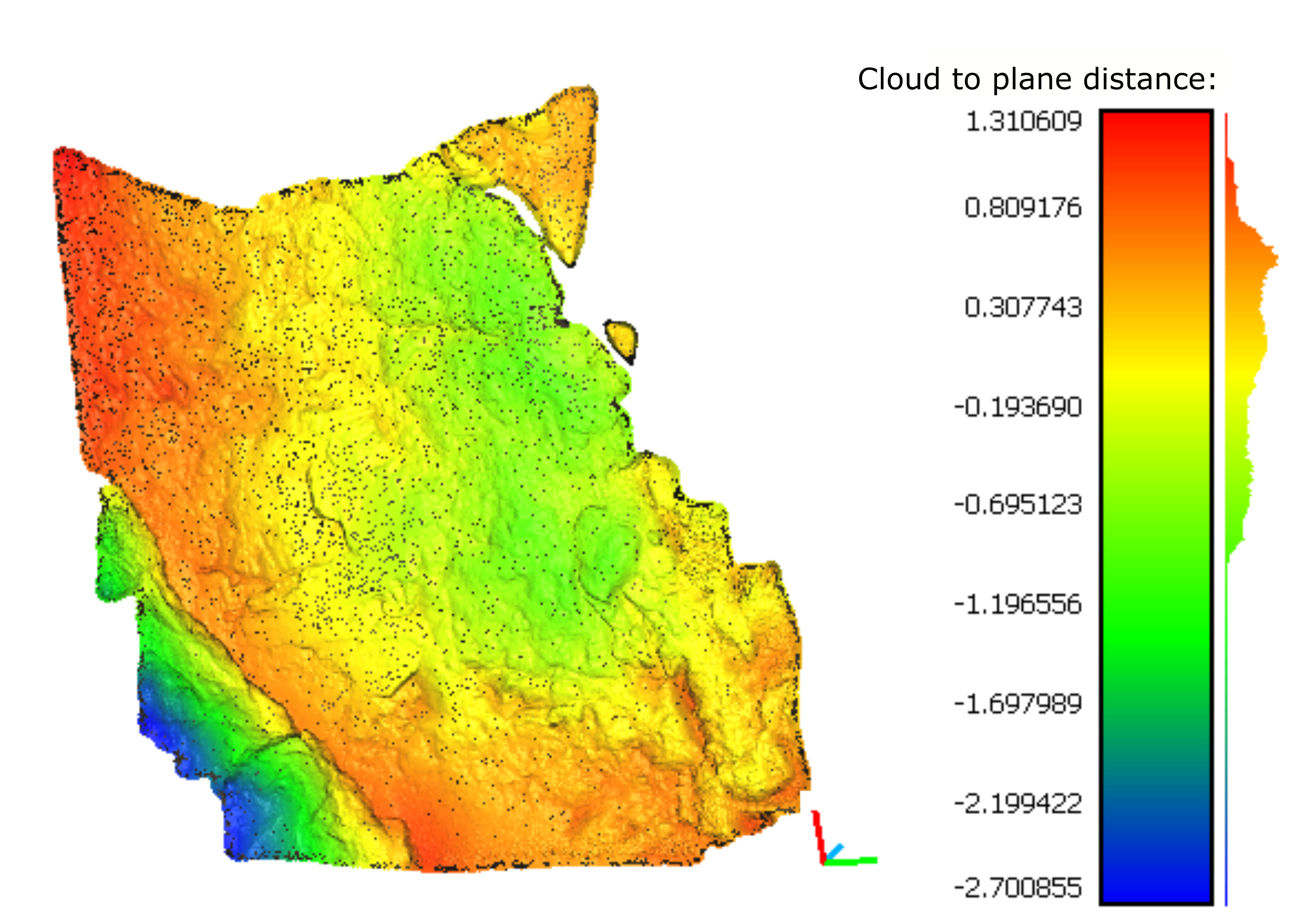
The acquisition of geological attitudes on rock cuts using traditional field compass survey can be a time consuming, dangerous, or even impossible task depending on the conditions and location of outcrops. The importance of this type of data in rock-mass classifications and structural geology has led to the development of new techniques, in which the application of photogrammetric 3D digital models has had an increasing use. In this paper we present two algorithms for extraction of attitudes of geological discontinuities from virtual outcrop models: ply2atti and scanline, implemented with the Python programming language. The ply2atti algorithm allows for the virtual sampling of planar discontinuities appearing on the 3D model as individual exposed surfaces, while the scanline algorithm allows the sampling of discontinuities (surfaces and traces) along a virtual scanline. Application to digital models of a simplified test setup and a rock cut demonstrated a good correlation between the surveys undertaken using traditional field compass reading and virtual sampling on 3D digital models.
Project Details
Date: Feb 27, 2016
Author: Viana, CD; Endlein, A; Campanha, GAC & Grohmann, CH
Categories: MSc
Tagged: Photogrammetry, SfM, Slope stability, Structural Geology
Journal/Event: Computers & Geosciences 90 (2016) 112-122
Website: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300416300516